By ; Basel Khaled- Mohamed El Kholy
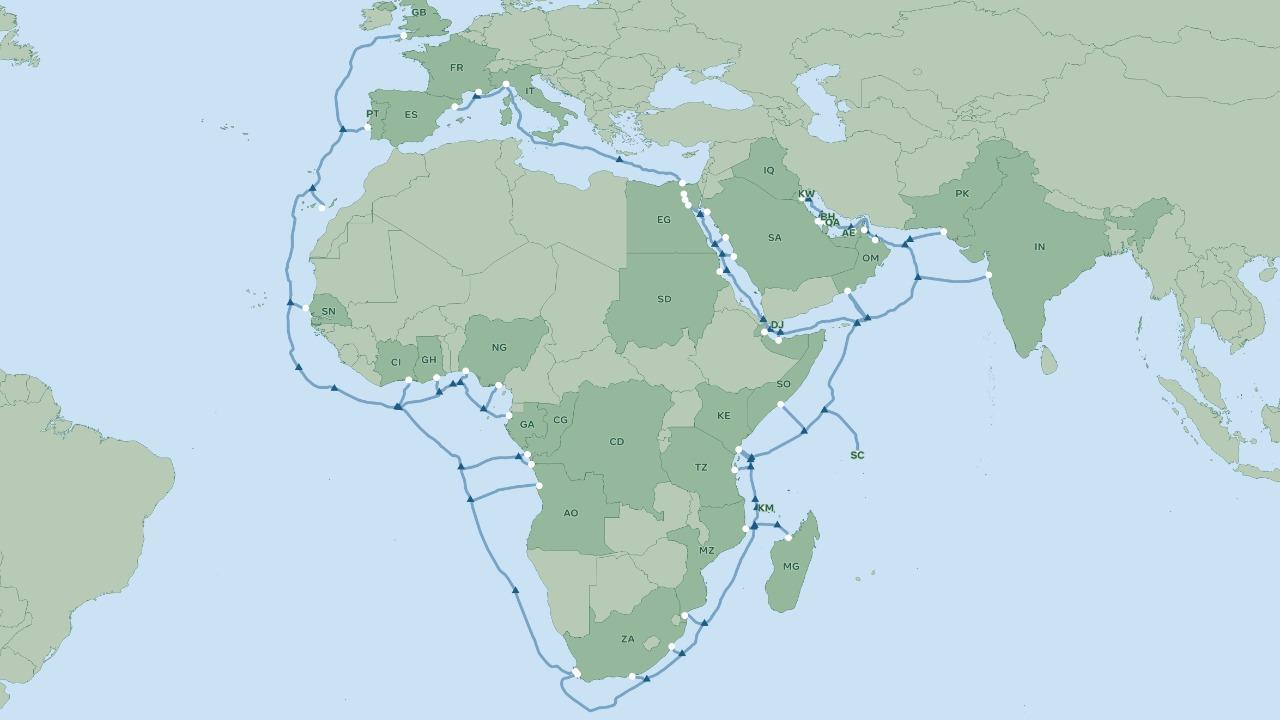
The 2Africa consortium, which includes China Mobile International, Facebook, MTN GlobalConnect, France's Orange, stc, Telecom Egypt, Vodafone International, African Telecom and IOC, was unveiled today. (WIOCC), announced the expansion of cable interconnection by adding the new segment 2Africa PEARLS to the Persian Gulf, India and Pakistan. This extension will increase the total length of the 2Africa submarine cable system to more than 45,000 km, making it the longest submarine cable system It is not implemented at all.
2Africa provides excellent connectivity services by connecting to three continents Africa, Europe and Asia via the land tracks of the Arab Republic of Egypt by adding vital landing sites in Barka in the Sultanate of Oman, Abu Dhabi and Kalba in the United Arab Emirates, Doha in Qatar, Manama in Bahrain, Kuwait City in Kuwait, and FAO in Iraq , Karachi, Pakistan, Mumbai, India, and a fourth landing site in Khobar, Saudi Arabia.
These sites will join the new landing sites in the Canary Islands, Seychelles, Comoros, Angola and southeastern Nigeria that were announced earlier. Internet ecosystem.
Through the new extensions, 2Africa cable will contribute to supporting the digital economy and enhancing the ability of many communities to provide more and more efficient internet-based services, such as education, healthcare and business services, and to achieve significant economic and social benefits as a result of this increased international connectivity.
The 2Africa submarine cable system was planned to provide interconnection services to over 1.2 billion people when it was announced in May 2020, but with the addition of the new sector 2Africa PEARLS, international interconnection services will reach an additional 1.8 billion people bringing the total beneficiaries to 3 billion people, which is equivalent to 36% of the world's population.
Alcatel Submarine Networks (ASN) will implement the new system using the latest technologies such as SDM technology, which allows the use of a greater number of optical fibers up to 16 fiber pairs, twice what is provided by current technologies, which helps to provide greater capacities at lower costs. .